 address:201, Factory 6, Longhui Industrial Park, Fuqiao 3rd District, Xinhe Community, Fuhai Street, Baoan District, Shenzhen china
address:201, Factory 6, Longhui Industrial Park, Fuqiao 3rd District, Xinhe Community, Fuhai Street, Baoan District, Shenzhen china
Detailed analysis of flexible PCB manufacturing process
Today, with the rapid development of the PCB industry, flexible PCBs (printed circuit boards) are also developing rapidly, and the market share is increasing. Next, this article will analyze the manufacturing process of flexible PCBs in detail.
Table of contents:
Flexible PCB, flexible PCB, flexible PCB introduction, flexible PCB introduction, what is flexible PCB, what is flexible PCB, the application of flexible PCB, the manufacture of flexible PCB, the manufacturing process of flexible PCB

What is a flexible PCB?
Originally, PCBs were designed using rigid substrate materials and thus were only available in rigid form (board/card form). As the technology was researched, scientists felt the need for PCBs that could be easily bent or folded to be placed in difficult locations, which gave rise to the idea of flexible PCBs. First introduced in 1950, flex PCBs serve two main purposes:
For products placed on irregular surfaces, such as keyboards.
Take advantage of the flexible area of the product, the smartwatch.
Flexible PCB Definition
A flexible printed circuit board (also known as a flexible printed circuit board/flexible printed circuit board (FPC)) is an advanced printed circuit board that has the ability to bend, twist or fold into any shape.
This is an incredible addition to the electronics industry as it takes up less space and is very lightweight.
Rigid PCBs are relatively easy to handle, while handling flex PCBs requires additional protocols (special clamping, material handling, etc.), which is why flex PCBs are generally more expensive compared to other types of PCBs.
In some electronics projects, flexible and rigid PCBs are combined to produce a unified product, such PCBs are called Rigid-Flex PCBs
Flexible PCBs are often used in wearable electronics because they stick easily to the body.
Flexible PCB Key Points
Flexible PCBs are not that simple/cheap and are usually designed by companies for their electronics. The flexible material should not be too bent or too rigid to damage the PCB when folded or twisted around corners. Complex flexible products utilize roll-to-roll technology involving advanced material handling techniques.
Why do we need flexible PCBs?
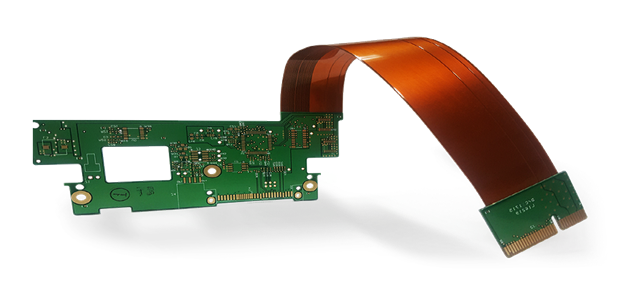
Before flexible PCBs, electronics were designed using rigid PCBs, and in a few products (such as watches), the space of rigid PCBs is almost negligible compared to their full size (including watch straps). In order to utilize these parts of electronics (for adding additional technology/circuitry), flexibility needs to be brought into the electronic PCB to accommodate any shape or location, hence the need for flexible PCBs.
Flexible printed circuit boards also allow electronics to be carried around, ie flexible computer keyboards. Just roll it and put it in your laptop bag. Flexible PCBs are also used in the oil and gas sector due to their ability to withstand high temperatures.
So, now let's take a look at the manufacturing process of a flexible PCB:
Flexible PCB Manufacturing Process
The flexible PCB manufacturing process involves almost the same steps as multi-layer PCBs, although it involves more specialization and expertise. Let's take a look at the steps of the flexible PCB manufacturing process:
Step 1: Design the CAD Model of the Flex PCB
Computer-aided design (CAD) models of flexible PCBs are designed by professional designers.
Circuit design for flex PCBs involves multiple teams as there are many factors to decide.
In addition to designing electronic circuits, designers must also pay attention to mechanical construction and chemical materials, as stretching or excessive bending can damage the circuit board.
Step 2: Find a Flexible PCB Manufacturer
This is the most important step, because we cannot design the flex PCB by ourselves, we have to ask the PCB manufacturing company for help. Therefore, designers should be very careful when choosing a PCB manufacturer.
Step 3: How to Make a Flexible PCB?
Flexible PCBs are manufactured by PCB companies that take orders from users (usually designers) and deliver them according to specified instructions. Following are the steps involved in the flex PCB manufacturing process:
Cut: According to the specified size in the flexible design.
Drilling: Drilling and through holes (in the case of multiple layers).
Electroplating: It involves placing copper tracks or paths.
Etching: Chemical treatment of Flex PCBs.
Trim: There is very little flex PCB trim involved, i.e. junctions.
Coating: Lamination of Flex PCB.
Pressing, solidification, punching, quality assurance
Step 4: Flex PCB Testing
The flex PCB testing is carried out after receiving the order from the PCB company.
It is usually tested in prototype projects.
Advantages of flexible PCB
1. Small size
Small size is the main advantage of flexible PCBs, even in some cases, flexible PCBs can be simply rolled and adjusted in tight spaces.
As a simple piece of paper, their width is negligible.
2. Lightweight
Flexible PCBs are very lightweight because there is no cardboard (substrate core) in them.
Usually its weight is due to the presence of SMD components in it.
3. High durability
When handled properly, flexible PCBs generally have a long service life because they are manufactured under precise conditions and in the presence of experts, and it is also coated with formulated materials that enhance its durability.

4. High temperature
It can withstand high temperatures, so it can be used in oil and gas fields where rigid PCBs can melt. Temperature resistance depends on the material used to design it.
5. Build capacity
Flexible printed circuits help improve the overall performance of electronic products by increasing component density.
Using flexible components, we can add more circuits to our autonomous products, enhancing their functionality.
Application of flexible PCB
Although flex PCBs are not common, they are only used for specific applications. Some Flex PCB applications are as follows:
1. Wearables
Flex PCBs are commonly used in electronic wearable devices such as watches, lockets, spy microphones, smart cameras, etc.
2. Electronic gadgets
Flexible PCBs are also used in electronic products such as cell phones, computer keyboards, CD/DVD drives, etc.
3. Connector
Connectors for expensive electronics are often designed using Flex PCBs.
Flexible connectors avoid wiring and connection problems.
4. Printer
The printer's moving printhead utilizes a flex circuit that provides a path to connect the signals to the moving arm of the disk drive.
6. Consumer Electronics
Flexible circuits are integrated into many consumer electronics products, including calculators, cameras, personal entertainment devices, and motion monitors.
7. Solar Technology
Flexible solar cells, another new addition to the field of flexible electronics, are lightweight and can be folded or twisted into any shape, primarily for powering satellites.
-
No comment












 tel:+86-18825224069
tel:+86-18825224069 email:
email:





















